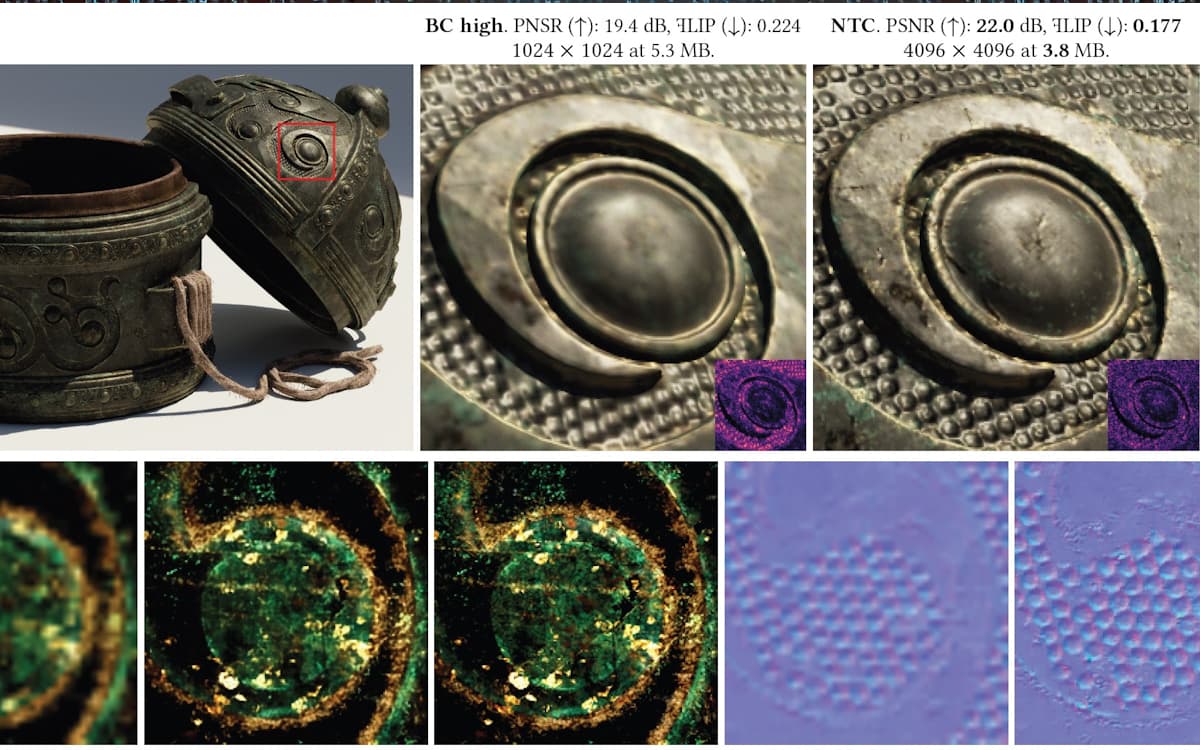
NVIDIA has made impressive advances in the field of texture compression with o RTX Neural Texture Compression (NTC). In tests performed by Compusemble, the technology demonstrated a up to 96% reduction in memory consumption for texturesenabling greater efficiency in GPUS, but with a slight impact on performance.
The tests were conducted with a RTX 4090 at 1440p and 4K resolutions, using different modes of neural compression.
As a result, the “NTC Transcoded to BCN” mode presented a significant reduction of 64% in memory consumption, while the “Inference on Sample” mode reduced consumption to impressive 11.37 MB – 95.8% lower than traditional methods of compression.
Values demonstrate the potential of the NTC to revolutionize memory management for textures in 3D applications. Look:
How RTX NTC works and its operating modes
In the tests performed on a RTX 4090, Compusemble used two main modes: “NTC transcoded to BCn” e “NTC inference on sample”.
- Or mode “NTC transcoded to BCn” It converts textures to the BCN format into loading, resulting in a 64% reduction in memory consumption. In a specific test, the use of Vram was reduced from 272 MB to 98 MB in this mode.
- Already the mode “NTC inference on sample”which decomposes only the texts necessary for the rendering of each scene, reached a minimum consumption of 11.37 MB, representing a 95.8% reduction compared to conventional compression.
The difference between the two modes also has a consequence of performance. THE “NTC transcoded to BCn” It had minimal impact on the frames per second (FPS), with minor improvements in 1% FPS falls. On the other hand, the “NTC inference on sample” presented perceptible drops in performance.

TEST RESULTS
1440p: DLSS vs TAA
With DLSS enabled in 1440p, the “NTC transcoded to BCn” maintained the performance close to the mode without compression, while the “NTC inference on sample” fell from about 1,600 fps medium to 1,500 fps. The impact was more evident in the minimum FPS values (1% Lows), which fell from 1,300 fps to 840 fps in the latter mode.
When the DLSS was replaced by TAA (time-based anti-aliasing), all modes operated significantly faster, reaching nearly 2,000 fps in the “NTC transcoded to BCn”. Or mode “NTC inference on sample” It had a substantial improvement, reaching minimum FPS values in the 1,300 FPS range.
4K: DLSS and Native Resolution
Increase resolution to 4K brought larger challenges. With DLSS enabled, the average performance was about 1,100 fps in mode “NTC transcoded to BCn” and just below 1,000 fps in mode “NTC inference on sample”. The minimum FPS values fell to the 500 FPS range in both modes.
Interestingly, by disabled DLSS in favor of native resolution with TAA, the average performance in mode “NTC transcoded to BCn” rose to 1,700 fps, while the “NTC inference on sample” It remained in the range of 1,500 fps.

Cooperative vectors
In the final test, Compusemble used 4K cooperative vectors with mode “NTC inference on sample”. With the functionality activated, the average performance was about 1,500 fps, while deactivation reduced the average to less than 650 fps.
The minimum values followed a similar trend, falling from 750 fps with vectors activated to just above 400 fps without them.
Impact on performance
Although NTC is a promising innovation, there is a performance cost, especially in Inference on Sample.
As we saw in the tests, the frames per second (FPS) fell from about 1,600 to 1,500 fps in 1440p resolution with enabled DLSS. In 4K, the performance also suffered falls at the minimum FPS values, demonstrating the high demand imposed on GPU tensor nuclei.
RTX Neural Texture Compression technology has the potential to redefine how 3D games and applications manage textures, but there are still challenges to be faced, especially in the balance between efficiency and performance
The performance impact has already been observed in other NVIDIA technologies, such as the Frame Generation do NVIDIA Reflex 2which initially only supports GPUS from the RTX 50 series due to the high processing requirement.
In addition, the company has been optimizing its technologies to reduce the load on the GPU, as happened with the updated version of the RTX Video Super Resolutionwhich now requires 30% less processing capacity.
Also read:
Potential and compatibility
Another point that draws attention in NTC is its wide compatibility, covering from GPUS from the RTX 20 series to older models such as GTX 10, as well as AMD and Intel plates. This opens the doors for the use of technology on more affordable platforms and even on consoles in the future.
Evolution positions RTX NTC as the biggest advancement in texture compression since the 1990s, allowing textures up to four times more resolution without demanding proportional.
However, while the impact on performance is not mitigated, the Technology follows in beta phase and without forecast of official release.
Fonte: Compusemble
Source: https://www.adrenaline.com.br/nvidia/rtx-neural-texture-compression-reducao-vram-tecnologia-nvidia/