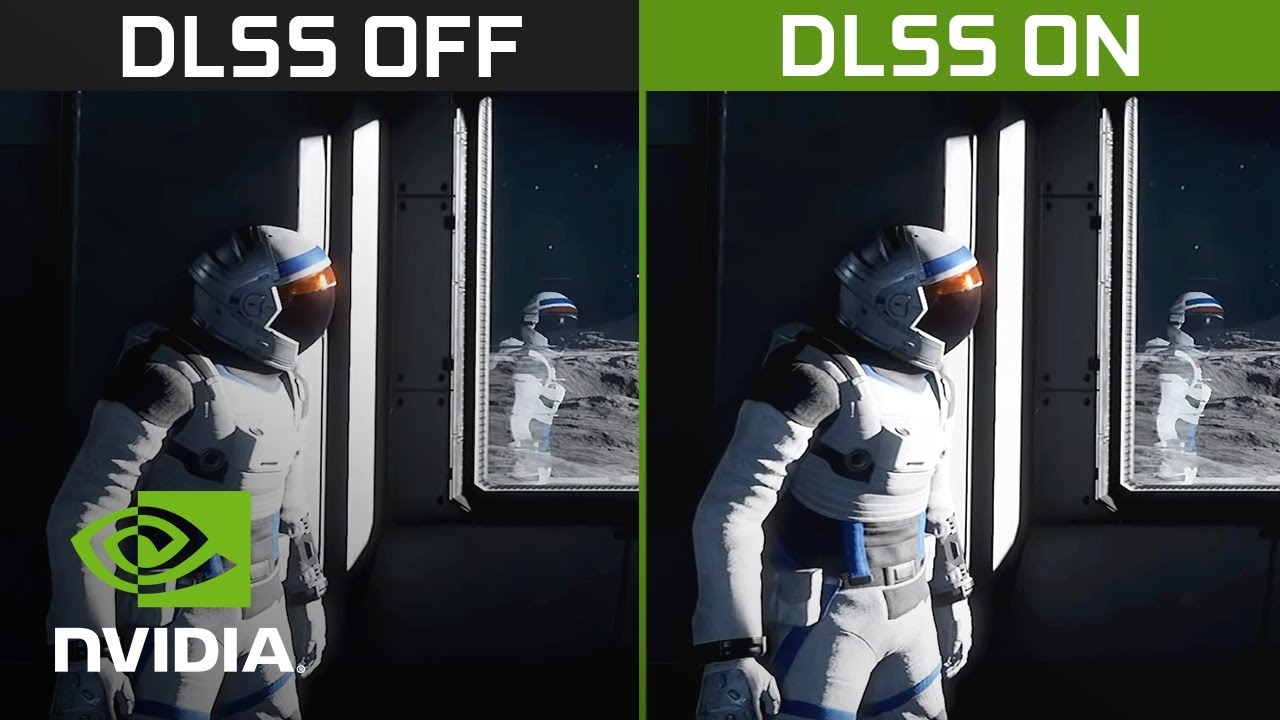
DLSS is the acronym for Deep Learning Super Samplingwhich, in literal translation means something like “Super Sampling with Deep Learning”. It is a technology created by NVIDIA that combines artificial intelligence (AI) with machine learning to improve video game performance without compromising graphic quality.
It was developed to work only with NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX graphics cards, which contain special cores, called Tensor Corescapable of carrying out complex AI processes. Back in 2018, when NVIDIA introduced the first RTX cards and the Ray Tracing feature, it was realized that the hardware alone would not be enough to guarantee acceptable performance in heavy games. Thus, DLSS was born as a fundamental reinforcement for these scenarios.
In the next paragraphs you can see how DLSS works, what its versions are and also what its benefits are for current games.
How does DLSS work?
The concept behind DLSS is simple, but its execution is quite sophisticated. Instead of rendering the game in high resolution, DLSS uses a technique called upscaling. When using this technique, the game image is rendered at a lower resolution and then upscaled to the desired resolution using AI.
This considerably reduces the workload on the GPU, increasing the number of frames per second (FPS) that the game can display. NVIDIA trains its AI with supercomputers to improve accuracy in image reconstruction, ensuring that the final result has visual quality very close to native resolution.
In practice, imagine that you want to play in 4K, but the graphics card doesn’t have enough power to deliver good FPS. DLSS renders the game at a lower resolution, such as Full HD (1080p), and then upscales that image to 4K. This amplification is done very efficiently by Tensor Cores, which use complex algorithms to fill in the missing details. The result is a high quality image and much smoother gameplay, with a higher FPS rate.
DLSS versions and modes
Since the release of the first version, DLSS has undergone several significant improvements. Below you can see an* overview* of each of the versions released to date.
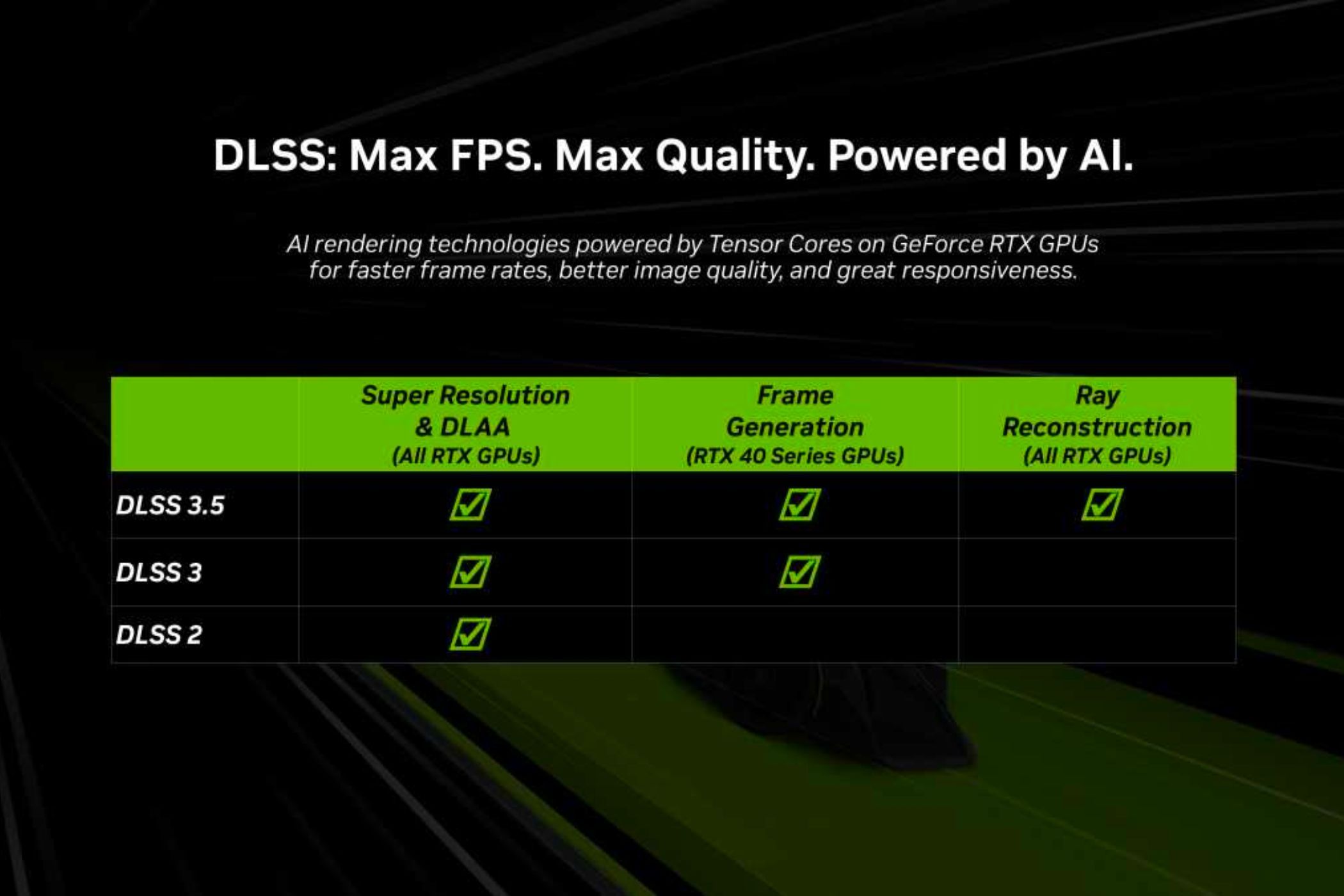
DLSS 1.0
Introduced in 2018, DLSS 1.0 used trained neural networks to upscale images rendered at low resolution to higher resolutions. Although it provided performance gains, image quality did not always meet expectations, presenting visual artifacts and lack of sharpness in some cases. Additionally, implementation required specific training for each game, limiting its adoption and effectiveness.
DLSS 2.0
Released in 2020, DLSS 2.0 brought substantial improvements. It adopted a generalized neural network, eliminating the need for individual training for each title. This version improved image quality, offering results closer to native rendering, and significantly increased performance. DLSS 2.0 also introduced different quality modes, allowing users to choose between Quality, Balanced, Performance and Ultra Performance, adapting the technology to their preferences and available hardware.
DLSS 3.0
Announced in 2022, DLSS 3.0 introduced frame generation (Frame Generation), a technique that creates intermediate frames using AI, doubling or even tripling the frame rate per second. This functionality is enabled by the new Tensor Cores and Optical Flow Accelerator present in RTX 40 series GPUs. DLSS 3.0 analyzes consecutive frames and calculates the flow of pixel movement, allowing the creation of additional frames that improve fluidity and performance of games.
DLSS 3.5
Released in 2023, DLSS 3.5 introduced the Ray Reconstructiona neural rendering technique that improves image quality in intensive ray traced content. This technology replaces manually adjusted denoisers with an AI network trained on NVIDIA supercomputers, generating higher quality pixels among the sampled rays. Ray Reconstruction is available for all GeForce RTX GPUs, improving visual fidelity and lighting accuracy in supported games.
As we mentioned above, DLSS also offers different modes for the user to choose according to their preferences: Quality, Balanced, Performance e Ultra Performance. These modes allow the player to prioritize image quality or performance depending on available hardware and desired experience.
Quality mode, for example, focuses on maintaining an image very close to native, while Ultra Performance mode is recommended for those who want to maximize the FPS rate, even if this implies a noticeable reduction in visual quality.
Benefits of DLSS for games

In addition to significantly improving the frame rate per second, DLSS also reduces the workload on the GPU and CPU, allowing both components to operate at lower temperatures and with lower power consumption.
This translates into greater component longevity and attractive cost-benefit for those looking for high gaming performance. Another important benefit is the improvement in edge smoothness (anti-aliasing), which is especially advantageous at lower resolutions, where aliasing is more evident.
Additionally, DLSS 3.5 introduced a new technique called Ray Reconstructionwhich improves the look of Ray Tracing in games by reducing noise and making lighting more realistic. Thus, in addition to increasing performance, DLSS contributes to a much more immersive graphical experience.
Comparison with other technologies

While NVIDIA pioneered DLSS, other companies have also developed upscaling solutions to improve the gamer experience. AMD, for example, offers the FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR)which is an open alternative and works on a wide range of GPUs, including those from NVIDIA.
Intel also entered the market with the XeSSwhich uses a similar approach to DLSS. However, DLSS stands out for its use of Tensor Cores, which provide a higher level of performance and more consistent image quality compared to alternatives.
DLSS is one of the most important technologies for modern games, allowing gamers to enjoy extremely high-quality graphics without compromising performance. With the advancement of versions, NVIDIA managed to transform DLSS into an essential solution for those who want to get the most out of their GPUs, especially in titles that make extensive use of Ray Tracing.
Source: https://www.hardware.com.br/artigos/dlss-melhora-desempenho-jogos/